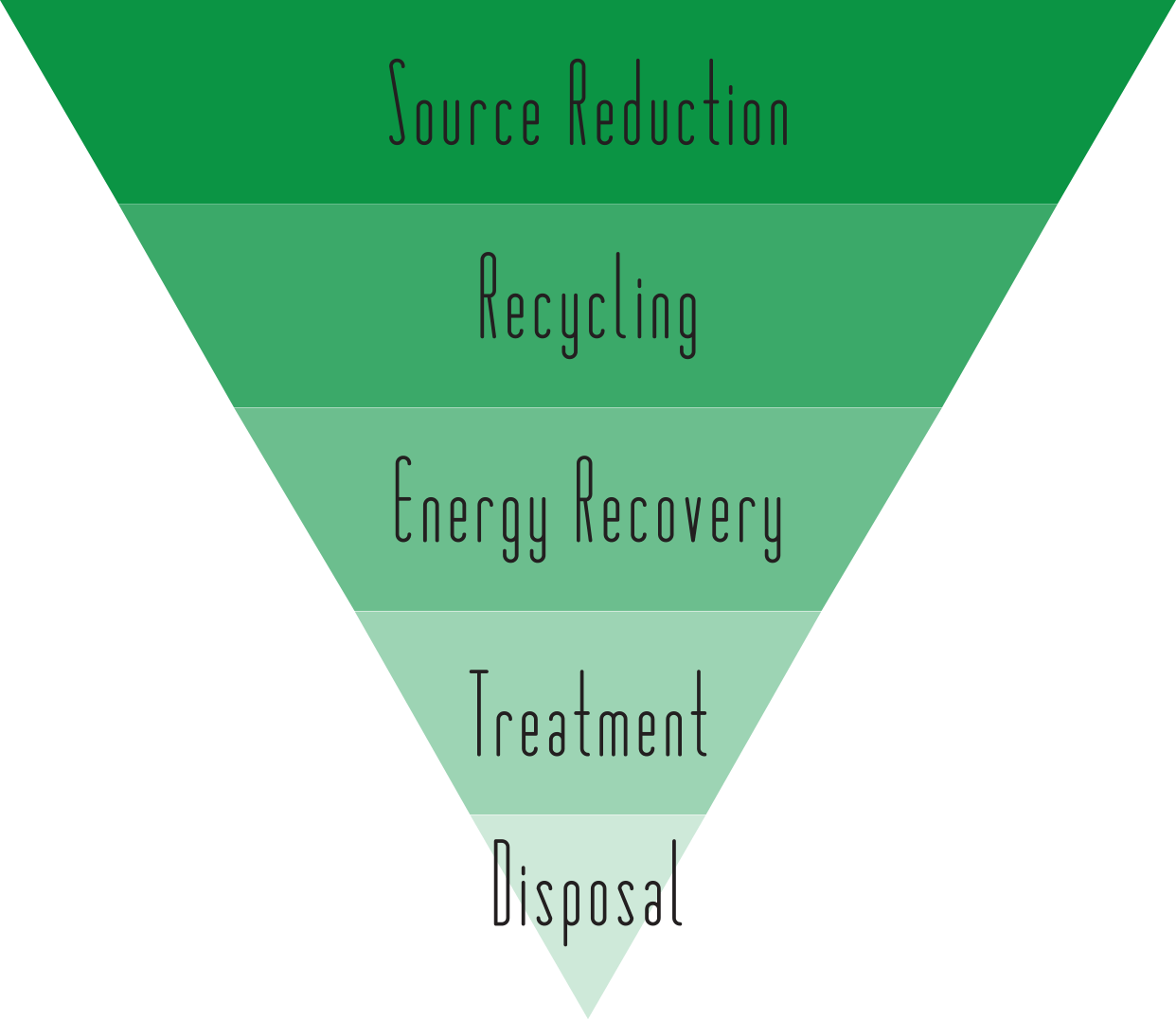
A couple of weeks ago we did a post on how the government is addressing waste minimization. Here we’ll talk more about what waste minimization is. According to the EPA, “Waste Minimization refers to the use of source reduction and/or environmentally sound recycling methods prior to energy recovery, treatment, or disposal of wastes.” Ergo, treatment of a wastestream does not constitute waste minimization. The EPA takes this further by clarifying that “compacting, neutralizing, diluting, and incineration are not typically considered waste minimization practices.” So in the hierarchy of materials management source reduction and recycling come before energy recovery, treatment, or disposal.
What is Source Reduction?
Source reduction (which is also known as pollution prevention or P2) is a practice that reduces or eliminates the creation of wastes at the source. Additionally, source reduction “refers to any practice that reduces the use of hazardous materials in production processes.” The EPA lists the following examples of source reduction:
- “Early retirement of equipment such as mercury-containing devices like switches and thermostats;
- Reformulating or redesigning products, such as creating new PVC compounds without using lead;
- Using less toxic feedstocks, such as switching to the use of lead-free solder in manufacturing;
- Improving work practices, such as reorganizing paint batches in order to reduce cleaning operations.”
How is Recycling Utilized?
While most of us know about recycling from a personal standpoint we probably still can learn about recycling at the manufacturing level. In most cases recycling is used when source reduction is not seen as practical economically. In the manufacturing process, “Recycling includes the reuse or recovery of in-process materials or materials generated as by-products that can be processed further on-site or sent offsite to reclaim value. Recycling is a broad term that encompasses the reuse of materials in original or changed forms rather than discarding them as wastes. Recycling can also be thought of as the collection and reprocessing of a resource so it can be used again, though not necessarily for its original purpose.” The EPA provides a few examples of the types of recycling that can be used for waste minimization:
- “Direct use/reuse of a waste in a process to make a product, such as reusing a purge product used to clean paint lines rather than disposing of it by incineration.
- Processing the waste to recover or regenerate a usable product, such as collecting vapor from dry cleaning operations, turning it back into liquid, and reusing the liquid to clean more clothes.
- Using/reusing waste as a substitute for a commercial product. When mercury is recycled from old equipment like switches, it can be used in new products that still require mercury, such as fluorescent bulbs. Recycling of mercury has been so successful that there is now enough recycled mercury in the U.S. that manufacturers do not need to use new mercury from mines.”
How can Waste Minimization help companies?
Aside from being good for the environment, waste minimization can help companies on an economic sense by eliminating wasted materials, improving production efficiency, and improving product quality. Additionally, the EPA states that “reducing waste generation through waste minimization has helped some companies change their RCRA regulatory status from large quantity generator (1000 or more kilograms of hazardous waste generated per month) to small quantity generator (between 100 and 1000 kg of hazardous waste generated per month), or to conditionally exempt small quantity generator (up to 100 kg of hazardous waste generated per month). Some have managed to eliminate the generation of hazardous waste and avoid RCRA regulatory requirements altogether.”
What do you think about waste minimization? Does your company have plans and processes in place to achieve waste minimization goals? Have you seen a good ROI on your efforts? We’d love to hear about it in the comments section!
Quoted and cited information (unless otherwise noted) for this blog post was gathered from the EPA FAQ Page on Waste Minimization. As always, this blog post is not intended to be comprehensive and it is always best to check with the EPA and local government for full, up-to-date, rules and regulations.
More News From Heritage
-
2/21/25
Heritage Announces East Liverpool, Ohio 2025 Environmental Grant Program
Learn about our East Liverpool Ohio grant opportunity!
-
2/18/25
Heritage Environmental Services Announces James (Shelby) Marlow as Chief Financial Officer
Heritage Environmental Services announced today that James (Shelby) Marlow will join the organization as Chief Financial Officer.
-
1/31/25
January Community Engagement Initiative: Home/Work Energy Reduction
Learn about our January community engagement initiative
-
1/29/25
Heritage Environmental Services Announces Chris Ebeling as Chief Commercial Officer
Heritage Environmental Services announced today that Chris Ebeling will join the organization as Chief Commercial Officer.
-
1/28/25
Heritage Environmental Services Addresses Industry Challenges with New State-of-the-Art Shredder
Heritage Environmental Services announced a new state-of-the-art shredding unit.
-
1/7/25
Navigating e-Manifest: What You Need to Know About Hazardous Waste Compliance
Learn about the e-Manifest Third Rule changes that begin January 22, 2025
-
12/23/24
Wreaths Across America 2024
This year, through collective effort and heartfelt generosity, we sponsored 727 wreaths and transported two truckloads of wreaths across the country.
-
12/2/24
Heritage Environmental Services Announces Rachel Evans as Chief Human Resources Officer
Heritage Environmental Services announced today that Rachel Evans will join the organization as Chief Human Resources Officer.








