Did you know that in 2013 the world consumed about 90.4 million gallons of oil each day [source]? Additionally, more than two thirds of the oil that is transported from producer to consumer is done so on supertankers via the sea. That means that annually almost 22 billion gallons of oil could end in a spill. And that doesn’t even take into account the oil that moves via underwater pipelines, offshore oil drilling rigs, coastal storage facilities, and refineries which also pose a risk. So with all that potential for danger, I started to wonder what an oil spill actually means for the environment (outside of knowing it’s bad) and how they can be best managed.
As Josh Clark of HowStuffWorks points out, “it’s fortunate that oil and water mix like, well, oil and water.” Because they don’t mix a spill will most always mean that a millimeter or so “slick” of oil will rest on the top of the water. Occasionally in fresh water heavy crude oil will sink. Once a spill happens time becomes the most important variable and helps to determine how a spill will be handled.
The EPA breaks oil spill cleanup methods into three different categories; Mechanical containment or recovery, chemical and biological methods, and physical methods.
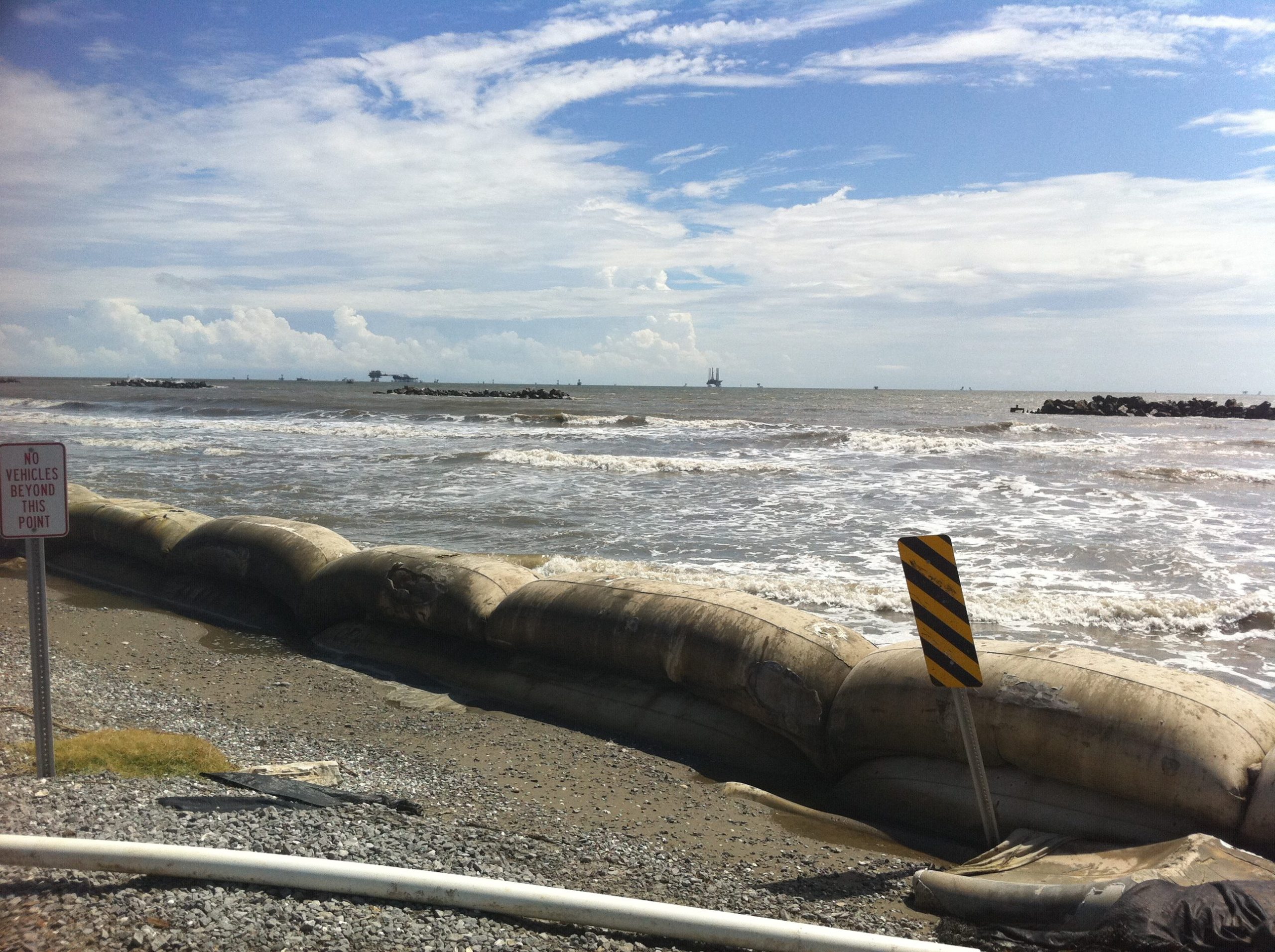
Mechanical containment and recovery is the most common method of cleanup. For example, if cleanup crews can get to the site of the spill within an hour or two (and if waves, weather, and currents have been cooperative) containment and skimming may be used. In this process large floating booms with skirts extending into the water are used to isolate the spill area and prevent the oil from spreading. Then the oil can be skimmed from the surface, sucked into tanks, and properly disposed of. Sorbent materials like peat moss, straw, hay, and sawdust may also be used in the processes to help absorb the oil.
According to the EPA, “chemical and biological methods can be used in conjunction with mechanical means for containing and cleaning up oil spills. Dispersing agents and gelling agents are most useful in helping to keep oil from reaching shorelines and other sensitive habitats. Biological agents have the potential to assist recovery in sensitive areas such as shorelines, marshes, and wetlands.”
If a spill is not stopped in time, or if it occurs close to the coast, physical methods will come into play. These methods are used to clean up shorelines. While natural processes like evaporation and oxidation will eventually get rid of spilled oil, the time it takes is far too long to allow. Because of this, “physical methods, such as wiping with sorbent materials, pressure washing, and raking and bulldozing can be used to assist these natural processes [source].” Biological agents can be used in these cases as well. For example, “fertilizers like phosphorus and nitrogen are spread over the oil-slicked shoreline to foster the growth of microorganisms, which break down the oil into natural components like fatty acids and carbon dioxide [source].”
The final step is to try to keep wildlife away from the spill area. This is done by employing things like floating dummies and balloons to frighten animals (and birds in particular) away from the site. Obviously this is not a foolproof tactic which is why controlling oil spills as soon as possible is vital.
If you would like more information about oil spill cleanup we highly recomend reading the sources sited in this post. The HowStuffWorks article, in particular, offers a great look into the process used for cleanups.